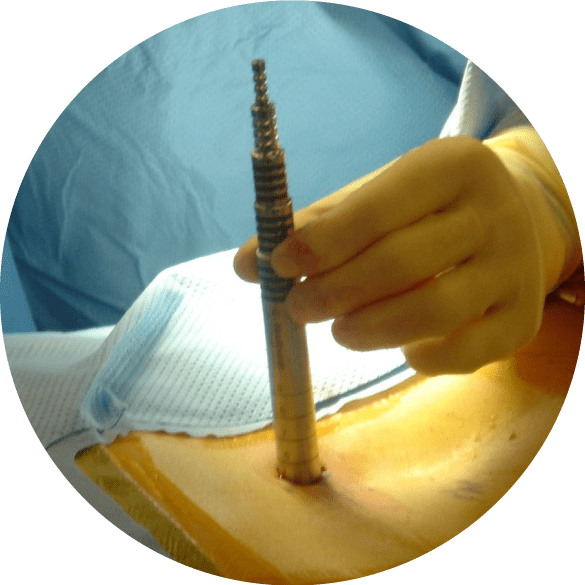
The goal of MISS is to achieve the same therapeutic outcomes while minimising trauma, reducing pain, shortening recovery times, and lowering the risk of complications associated with open surgeries.
Key features of minimally invasive spinal surgery include
MISS involves making smaller incisions compared to traditional open surgery. These incisions are typically less than an 2cm long, resulting in a better cosmetic outcome.
Surgeons use advanced microscopes, imaging techniques such as fluoroscopy or intraoperative robotic navigation, to visualise the affected area of the spine during the procedure. This allows for precise and accurate placement of instruments and implants.
Because MISS causes less trauma to the tissues, patients typically experience less postoperative pain and a faster recovery. They may be able to return to their regular activities sooner.
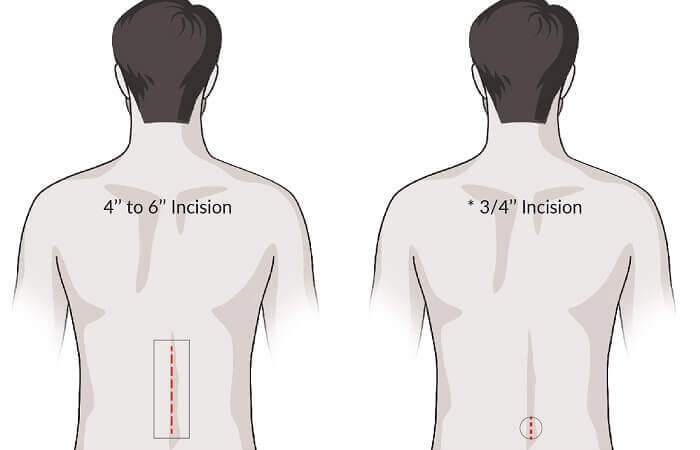
Minimally invasive spinal surgery generally has better results than open surgery, as there is a much greater accuracy in diagnosis and treatment of pain is very precise. For this reason, MISS is also a safer way to operate.
A number of specific techniques have been deployed for MIS surgery. Though the field continues to develop, the list below highlights some of the most common options.
MBBS, BMedSci, FRACS
Neurosurgeon & Spine Surgeon with 25+ Years Experience
He consults and operates from Sydney’s most advanced neurosurgical and spinal surgery hospitals, including St Vincent’s Private Hospital, Prince of Wales Private Hospital and The Mater Hospital.
These hospitals offer the latest neurosurgical facilities, including cutting-edge imaging equipment and surgical navigation systems, dedicated and well-trained theatre clinical staff, as well as post-surgical rehabilitation specialists.
A/Prof Parkinson’s areas of expertise include surgery of the entire spinal column, scoliosis surgery, peripheral nerve surgery, as well as physical rehabilitation of athletes that have suffered a brain or spine injury.
Please get in touch with our reception team if you have a general enquiry for A/Prof Parkinson, or your would like to book an appointment.

Office open hours are between 8:30am to 4:30pm. Please call to make an appointment.
Copyright © iSpine 2024